Melasma:
Have you ever noticed dark patches on your cheeks or forehead that seem to get darker every time you step out in the sun—even with sunscreen on? If so, you’re not alone.
Melasma is one of the most common yet misunderstood skin conditions, affecting millions—especially women in their 20s to 40s. It’s harmless, but emotionally draining. Those stubborn brown or grayish patches can affect your self-esteem, even if your skin is otherwise healthy.

Why You’ll Love This Guide:
- Expert-approved treatments that work fast and safely
- Natural remedies you can try at home with confidence
- Long-term prevention tips to keep pigmentation from coming back
- Real dermatologist insights to help you make smarter skincare choices
Let’s break down melasma step by step and guide you toward clearer, more even-toned skin.
Understanding Melasma: What It Is and Why It Happens
What is Melasma?
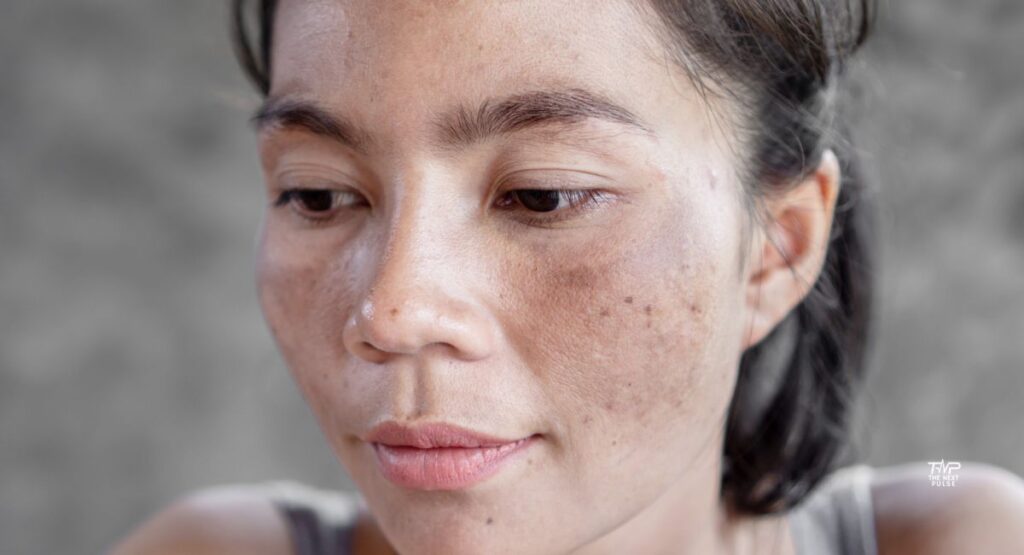
Melasma is a chronic pigmentation disorder that leads to brown, gray, or tan patches, primarily on sun-exposed areas of the face. It’s classified as a form of facial hyperpigmentation, and while it’s not medically harmful, it can be cosmetically distressing.
What Does Melasma Look Like?
- Color: Light to dark brown, gray-brown, or slate-gray patches
- Texture: Flat and smooth (not bumpy or flaky)
- Common Areas: Cheeks, upper lip, forehead, chin, bridge of the nose
- Symmetry: Often appears symmetrically on both sides of the face
Common Causes and Triggers:
| Trigger | How It Affects the Skin |
| Sun exposure | UV rays stimulate melanocytes, increasing pigment |
| Hormonal changes | Pregnancy, birth control, or hormone therapy can disrupt melanin balance |
| Genetics | Family history plays a major role in susceptibility |
| Heat & visible light | Non-UV heat and light can still trigger melasma |
| Certain medications or cosmetics | Can increase skin sensitivity or inflammation |
| Thyroid dysfunction | Associated with hormonal imbalance and pigmentation changes |
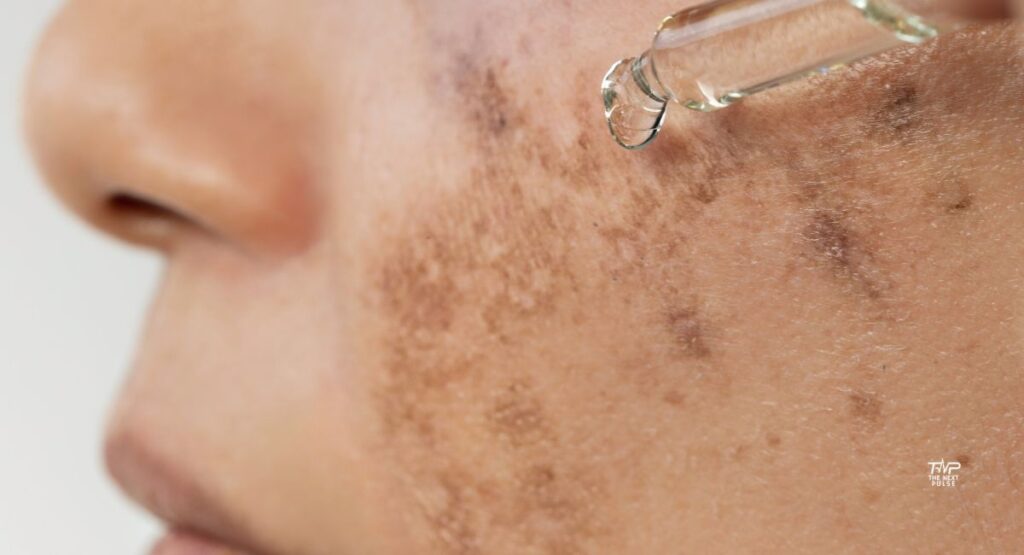
Dermatologist-Recommended Medical Treatments for Melasma
1. Prescription Topicals
- Hydroquinone (2–4%)
The gold standard for skin lightening. Inhibits melanin production.
Note: Use under dermatological supervision due to risk of irritation or ochronosis with prolonged use. - Tretinoin (Retin-A)
Accelerates cell turnover and helps fade hyperpigmented cells. - Corticosteroids
Reduce inflammation when used as part of triple combination therapy. - Azelaic Acid (15–20%)
Gently fades pigment and is safe for long-term use. - Tranexamic Acid (topical or oral)
Newer treatment that inhibits melanin formation at multiple levels.
2. In-Clinic Procedures
- Chemical Peels
Glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and lactic acid peels can help exfoliate and lighten patches.
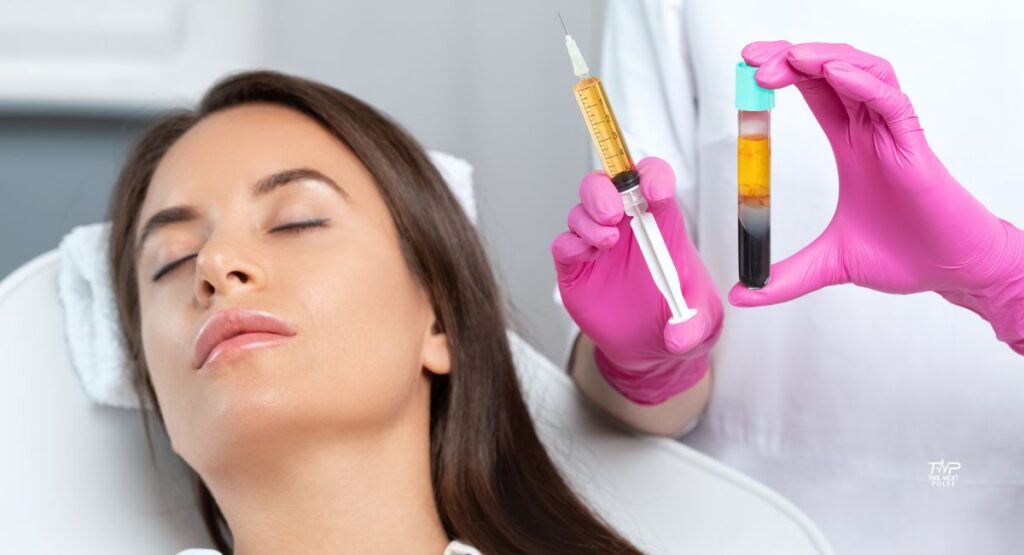
Frequency: Every 3–4 weeks in a clinical setting. - Microneedling with Tranexamic Acid
Improves product penetration and fades pigmentation. Its harmless according to Health Science Report. - Laser Therapy (e.g., Q-switched Nd:YAG or PicoSure)
Should be used cautiously. Can be effective, but there’s a high risk of rebound pigmentation if done improperly.
⚠️ Precaution: Melasma is sensitive and can worsen with aggressive treatments. Always consult a board-certified dermatologist for a tailored plan.
Home Remedies for Melasma (Backed by Science)
1. Aloe Vera
- Why it works: Contains aloesin, which inhibits melanin production.
- How to use: Apply fresh aloe vera gel twice daily.
- Results timeline: 6–8 weeks with regular use.
2. Turmeric Mask
- Why it works: Curcumin in turmeric has anti-inflammatory and melanin-reducing properties.
- DIY Mask: Mix 1 tsp turmeric with 1 tbsp yogurt or honey. Apply 2–3 times a week.
- Results timeline: 8–12 weeks.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) Toner
- Why it works: Acetic acid can help fade dark spots.
- How to use: Dilute 1:3 with water, apply for 5 minutes, rinse thoroughly.
- Caution: Always patch test first. Avoid on irritated skin.
4. Licorice Root Extract
- Why it works: Contains glabridin, a natural melanin inhibitor.
- How to use: Apply as serum or mix powder with aloe vera gel.
- Results timeline: Visible improvement in 4–6 weeks.
5. Green Tea Compress
- Why it works: Rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory catechins.
- How to use: Apply cooled green tea bags to the skin for 10 minutes.
⏳ Note: Natural remedies work gradually and are best used alongside medical treatments for enhanced results.
Additional Tips to Prevent & Manage Melasma
1. Sunscreen is Non-Negotiable
- Use broad-spectrum SPF 50+ with physical blockers (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide).
- Reapply every 2–3 hours, even indoors or on cloudy days.
2. Avoid Heat Triggers
- Limit exposure to saunas, steam rooms, and intense cooking heat.
- Use thermal spring water sprays to cool the skin post-exposure.
3. Gentle Skincare Routine
- Avoid aggressive exfoliants and harsh chemicals.
- Stick to calming ingredients: niacinamide, ceramides, hyaluronic acid.
4. Dietary Support
- Include foods rich in vitamin C, E, and polyphenols (berries, green tea, leafy greens).
- Hydration helps skin barrier function and healing.
💡 Pro Tip:
“Consistency is everything with melasma. Even the best treatments won’t work overnight. But with a strategic approach and proper sun protection, results are not only possible—they’re sustainable.”
— Dr. Ayesha M., Consultant Dermatologist



Final Thoughts:
Melasma can feel stubborn and overwhelming, but you don’t have to fight it alone—or guess your way through it. With the right knowledge, professional guidance, and daily habits, you can fade those dark patches and restore your confidence.
🧴 Your Action Plan:
Start by upgrading your sun protection game, consult a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan, and incorporate soothing, pigment-safe skincare into your routine.
1. Can stress cause melasma?
Yes. Stress can disrupt hormone levels and trigger or worsen melasma in hormonally sensitive individuals.
2. Will melasma go away after pregnancy?
In many cases, melasma may fade post-pregnancy, especially if it was hormonally triggered. But some pigmentation can persist without treatment.
3. Can I treat melasma permanently?
Melasma is chronic and relapsing, meaning it can be managed but not necessarily cured. Long-term maintenance is key.
4. Is it safe to use makeup over melasma?
Yes, but opt for non-comedogenic, fragrance-free products with built-in SPF. Always remove makeup thoroughly.
5. Can men get melasma too?
Absolutely. Although more common in women, men can develop melasma due to sun exposure, genetics, or medications.

Treat Stubborn Hyperpigmentation Naturally & Professionally
Dark patches, acne scars, random sun spots, darker patches on the skin—hyperpigmentation loves to show up uninvited and can make your complexion look uneven, dull, or prematurely aged. And the worst part? They take forever to move out. Doesn’t matter if it came from a pimple, pregnancy hormones, or just too much time outside, the result is the same: uneven skin that makes you feel older, duller, or just plain annoyed.
